Pleural effusion, or water on the lungs, is a condition where excess fluid accumulates between the pleura layers surrounding the lungs. You may not know, but it can cause symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and coughing. Effective treatment is essential for symptom relief and addressing the cause. In recent times, patients have access to various pleural effusion treatment in Delhi and advanced medical facilities.
Understanding Pleural Effusion
Pleural effusion happens when fluid builds up in the pleural space between the lungs and chest wall. The visceral pleura is the first layer that covers the lungs, and the parietal pleura lining the chest cavity is the second layer. Usually, a small amount of fluid between these layers helps with lubrication and breathing. However, certain conditions can lead to excessive fluid accumulation, causing pleural effusion.
Causes of Pleural Effusion
Pleural effusion can result from various medical conditions, and understanding the underlying cause is essential for determining the appropriate treatment. Common causes include:
- Heart Failure: This is where fluid builds up due to the heart’s inability to pump effectively.
- Infections: Pneumonia, tuberculosis, and other infections can lead to pleural effusion.
- Lung Cancer: Malignancies can cause fluid accumulation in the pleural space.
- Pulmonary Embolism: Blood clots in the lungs can contribute to pleural effusion.
- Liver or Kidney Disease: These conditions can cause fluid retention, leading to the same.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Rheumatoid arthritis and lupus are among the conditions that can cause fluid to build up in the space surrounding the lungs.
Symptoms of Pleural Effusion
The symptoms of pleural effusion can differ based on the volume and amount of fluid and the underlying cause. Common symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Cough
- Fever (in cases of infection)
- General discomfort or difficulty breathing
In some cases, pleural effusion may be asymptomatic, particularly when the fluid buildup is minimal.
Diagnosis of Pleural Effusion
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment of pleural effusion. Nowadays, patients can access advanced diagnostic facilities that offer a range of tests to identify the cause and extent of the condition.
Physical Examination and Medical History
The diagnostic process typically begins with a thorough physical examination and review of the patient’s medical history. The doctor will use a stethoscope to listen to the lungs for abnormal sounds that might suggest fluid buildup.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests are essential for visualizing the pleural effusion and assessing its extent. Common imaging tests include:
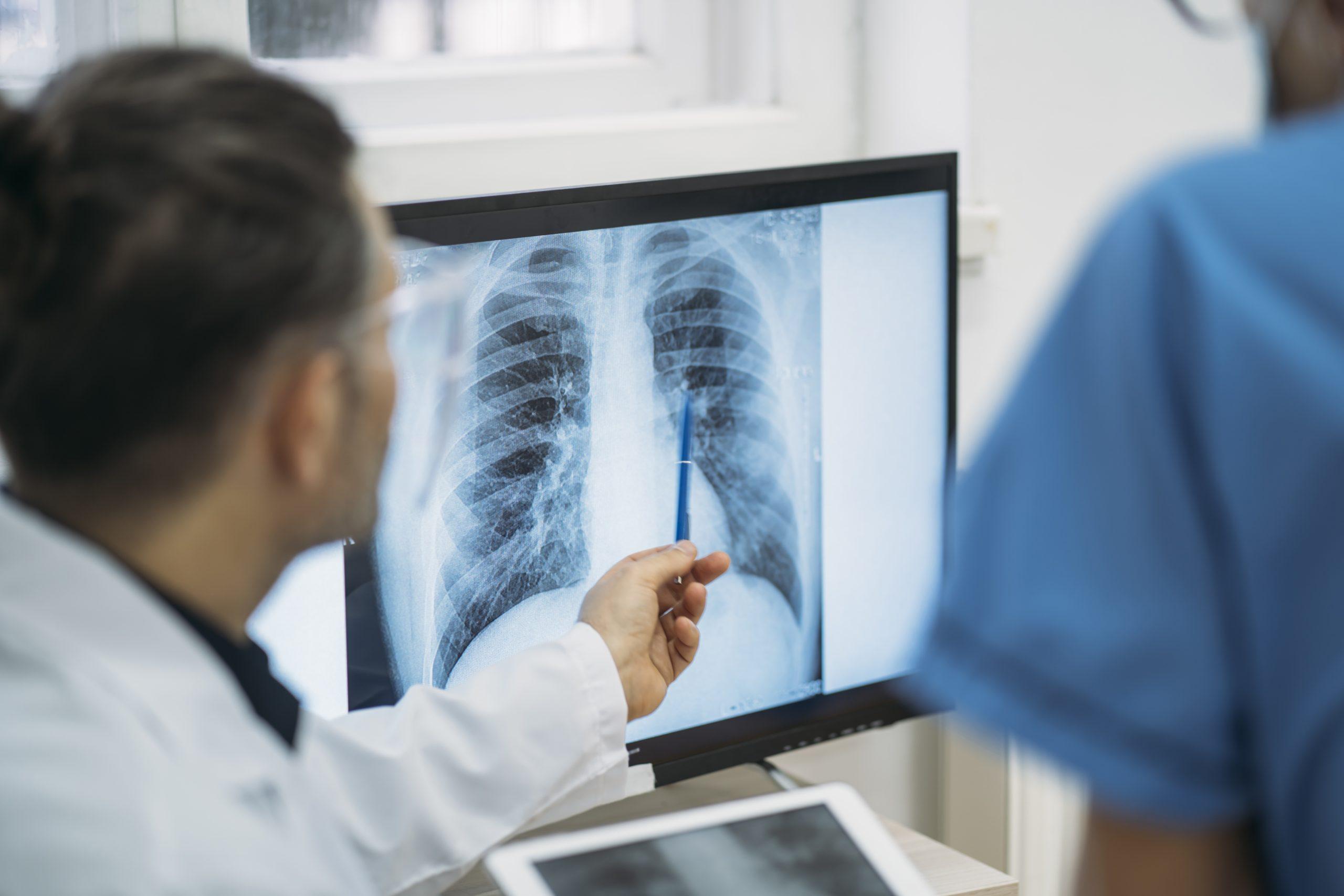
- Chest X-ray: Typically, a chest X-ray is the initial imaging test used to confirm the presence of pleural effusion.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound provides a more detailed view of the pleural space and helps guide procedures like thoracentesis.
- CT Scan: A CT scan offers cross-sectional images of the chest, providing a comprehensive view of the lungs and pleura. It is especially useful for identifying underlying causes like tumours or infections.
Thoracentesis
Thoracentesis is a diagnostic procedure in which a needle is inserted into the pleural space to remove a sample of fluid. The fluid is then analyzed to determine the cause of the effusion. This procedure can also be therapeutic, providing relief from symptoms by draining excess fluid.
Blood Tests
Blood tests can identify infections, autoimmune disorders, or other conditions contributing to pleural effusion. They provide a complete health overview and guide treatment decisions.
Treatment Options for Pleural Effusion
The treatment of pleural effusion depends on the underlying cause, the severity of the symptoms, and the overall health of the patient. There are many treatment options ranging from conservative management to more invasive procedures.
Treating the Underlying Cause
Addressing the underlying cause of pleural effusion is a primary goal of treatment. For example:
- Heart Failure: Medications will reduce fluid buildup as well as improve heart function.
- Infections: Antibiotics or antiviral medications will treat the underlying infection.
- Cancer: Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or surgery to treat lung cancer or other malignancies.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Immunosuppressive medications to manage conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
Thoracentesis
Thoracentesis is a common treatment for pleural effusion that involves the removal of fluid from the pleural space using a needle. This procedure not only provides symptom relief but also helps in preventing the recurrence of fluid buildup. In certain situations, multiple thoracentesis procedures may be required.
Pleurodesis
Pleurodesis is a procedure used to prevent the recurrence of pleural effusion, particularly in cases related to cancer. Here, a chemical agent is injected into the pleural space, causing the pleura to adhere to each other and removing the space where fluid can collect. This is often recommended when recurrent pleural effusion is expected.
Indwelling Pleural Catheter
An indwelling pleural catheter may be suggested for recurrent pleural effusion. This small tube, inserted into the pleural space, lets patients drain fluid at home. It is minimally invasive and offers symptom relief and improved quality of life for those with chronic effusion.
Surgery
In certain instances, surgery may be necessary to treat pleural effusion. Surgical options include:
- Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS): A minimally invasive procedure that allows the surgeon to drain fluid, take biopsies, and perform pleurodesis.
- Decortication: The removal of the thickened pleura that can develop in chronic pleural effusion cases.
Conclusion
Pleural effusion is a serious condition that needs prompt diagnosis and treatment. Healthcare providers can effectively manage pleural effusion and improve patient quality of life. If you suspect pleural effusion or have symptoms, seek medical attention promptly for proper care, or you can also get in touch with Dr. Arvind Kumar for better treatment.