Melanoma, the most aggressive form of skin cancer, has seen significant advancements in treatment over recent years. As awareness of skin cancer increases, so too does the need for effective treatment options. This article explores the latest advances in melanoma treatment Irvine CA, as well as a brief look at related conditions, including basal cell carcinoma treatment and cyst treatment. By understanding these developments, you can make informed decisions about skin health.
Understanding Melanoma: The Basics
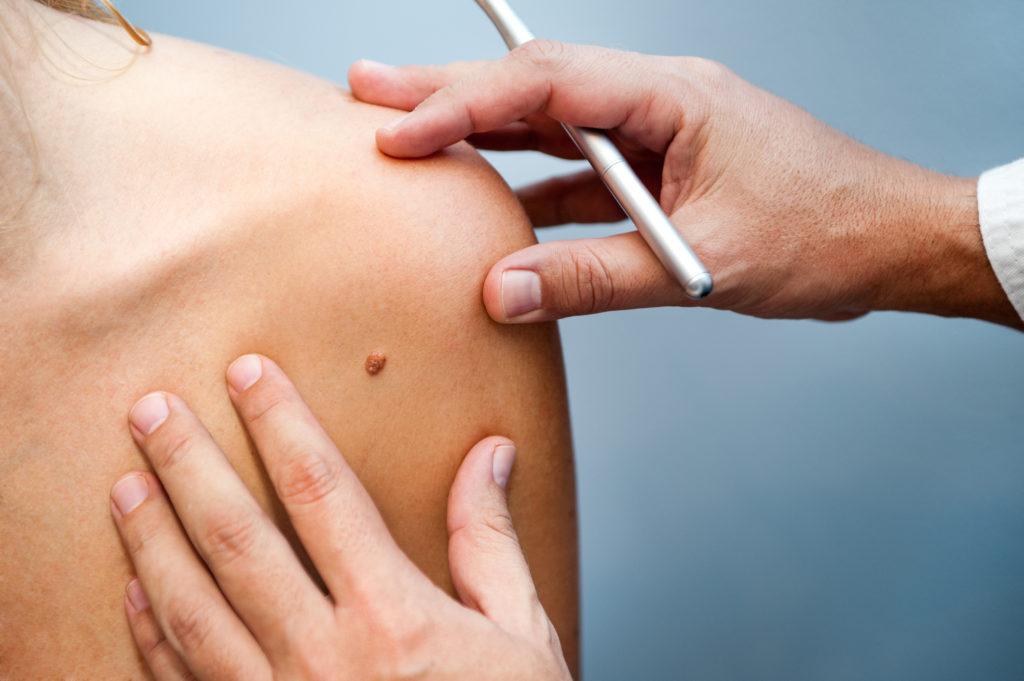
What Is Melanoma?
Melanoma originates in the melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. Unlike other forms of skin cancer, such as basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, melanoma can spread quickly to other parts of the body if not treated early.
Risk Factors for Melanoma
Understanding risk factors is essential for prevention. Some common risk factors include:
• Excessive sun exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) radiation can damage skin cells, leading to melanoma.
• Family history: A family history of melanoma increases your risk.
• Fair skin: People with light skin, red or blonde hair, and light-colored eyes are more susceptible.
• Moles: Having atypical moles or numerous moles can also increase risk.
The Latest Advances in Melanoma Treatment
- Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy uses drugs that specifically target cancer cells, minimizing damage to healthy cells. The two main targets in melanoma treatment are:
• BRAF Mutations: About 40-60% of melanomas have a mutation in the BRAF gene. Medications like vemurafenib and dabrafenib inhibit this mutation, slowing down cancer progression.
• MEK Inhibitors: Used in conjunction with BRAF inhibitors, drugs like trametinib can further enhance treatment effectiveness by targeting a protein involved in cell division.
- Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy has transformed the landscape of melanoma treatment by harnessing the body’s immune system to fight cancer. Recent advancements include:
• Checkpoint Inhibitors: These drugs, such as pembrolizumab and nivolumab, block proteins that prevent immune cells from attacking cancer cells. This allows for a more robust immune response against melanoma.
• Combination Therapy: Combining different immunotherapy drugs can lead to better outcomes. Research shows that using nivolumab and ipilimumab together can improve survival rates compared to single-agent therapies.
- Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine tailors treatment based on individual genetic and molecular profiles. New genomic testing methods allow oncologists to identify specific mutations in a patient’s tumor, guiding them to the most effective treatment options. This approach not only improves outcomes but also reduces unnecessary side effects.
- Radiation Therapy
While traditionally used for other cancers, radiation therapy is gaining traction in melanoma treatment, especially in cases of advanced disease. Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) delivers high doses of radiation precisely to tumors, minimizing damage to surrounding tissues.
- Clinical Trials
Participating in clinical trials can provide access to cutting-edge treatments not yet widely available. Ongoing research is focusing on new drug combinations, innovative delivery methods, and novel treatment approaches, such as CAR T-cell therapy, which genetically modifies a patient’s T cells to better attack cancer.
Related Conditions: Basal Cell Carcinoma and Cyst Treatment
While melanoma is the focus, it’s essential to be aware of other skin conditions, such as basal cell carcinoma and cysts.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Treatment
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer, usually appearing as a shiny bump or a flat lesion on sun-exposed areas of the skin. Treatment options include:
• Topical medications: Creams like imiquimod can be effective for superficial basal cell carcinoma.
• Mohs micrographic surgery: This technique removes cancerous cells layer by layer, ensuring complete removal while preserving healthy tissue.
• Cryotherapy: Freezing the cancerous cells can also be an effective treatment.
Cyst Treatment
Cysts are non-cancerous lumps that can occur in various parts of the body, including the skin. Treatment options include:
• Drainage: A healthcare provider can drain the cyst to relieve pressure and discomfort.
• Surgical removal: For larger or recurrent cysts, complete surgical removal may be necessary.
Tips for Skin Health and Early Detection
To reduce the risk of melanoma and other skin cancers, consider the following tips:
• Regular Skin Checks: Perform self-exams monthly and see a dermatologist annually.
• Sun Protection: Use broad-spectrum sunscreen, wear protective clothing, and avoid tanning beds.
• Stay Informed: Educate yourself about the signs of skin cancer, such as changes in moles or new growths.
Conclusion
The landscape of melanoma treatment is continually evolving, offering hope and new options for patients. Advances in targeted therapies, immunotherapy, and personalized medicine are changing the prognosis for those diagnosed with melanoma. Understanding these advancements can empower you to take charge of your skin health.
Additionally, being informed about other skin conditions, like basal cell carcinoma treatment Orange CA and cyst treatment, helps you understand your overall skin health better. Always consult with a qualified dermatologist for personalized advice and treatment options. By prioritizing skin health and staying educated, you can significantly improve your chances of early detection and successful treatment.