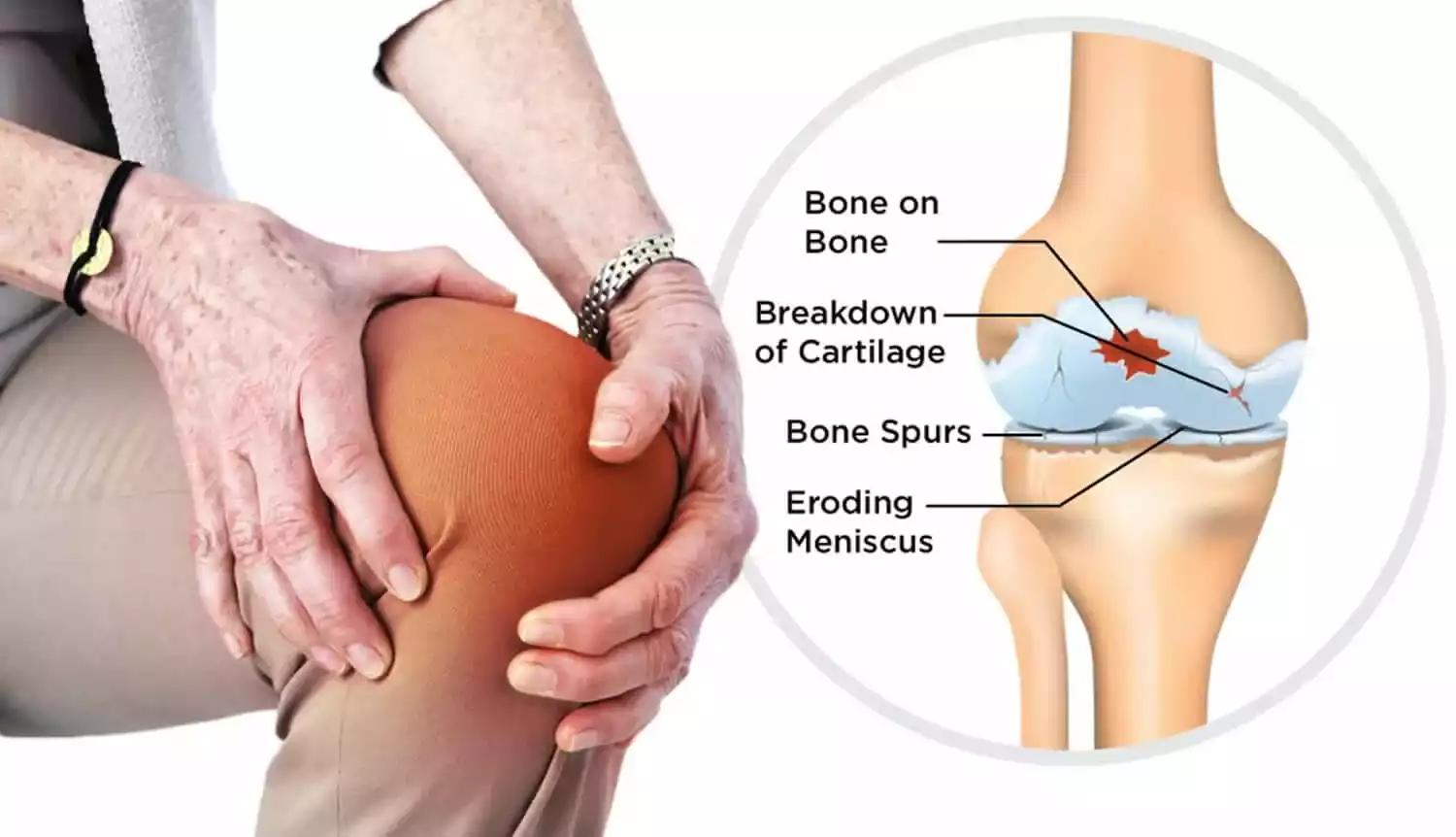
Osteoarthritis (OA) affects millions globally, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility primarily in weight-bearing joints such as knees, hips, and spine. Traditional treatments like pain medications and physical therapy offer relief but may not address the underlying damage to joint tissues. In recent years, stem cell therapy has emerged as a promising alternative, offering hope for regeneration and long-term improvement. Let’s delve into this innovative approach and its potential impact on managing osteoarthritis.
Understanding Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells capable of transforming into specialized cells, promoting tissue repair and regeneration. In the context of osteoarthritis, stem cell therapy aims to:
- Reduce Inflammation: Stem cells possess anti-inflammatory properties, which can alleviate swelling and pain associated with OA.
- Regenerate Cartilage: By stimulating the production of new cartilage tissue, stem cells may help repair damaged joints and improve overall joint function.
- Modulate Immune Response: Stem cells can interact with the immune system to promote a balanced response, potentially slowing down the progression of OA.
Types of Stem Cells Used
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs): These are commonly used due to their ability to differentiate into bone, cartilage, and fat cells. MSCs can be sourced from bone marrow, adipose tissue (fat cells), or umbilical cord tissue.
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs): iPSCs are reprogrammed adult cells capable of differentiating into various cell types, including cartilage cells. They offer a potentially unlimited source of patient-specific stem cells.
The Treatment Process
- Harvesting: Stem cells are extracted from the patient’s own bone marrow or adipose tissue. Alternatively, stem cells from a donor source may be used.
- Processing: The stem cells are then processed and purified in a lab to concentrate them before injection into the affected joint.
- Injection: The concentrated stem cells are injected directly into the joint under ultrasound or fluoroscopic guidance to ensure precise placement.
Effectiveness and Clinical Trials
Clinical studies have shown promising results regarding the efficacy of stem cell therapy for osteoarthritis:
- Pain Reduction: Many patients report decreased pain levels and improved joint function after stem cell treatment.
- Cartilage Regeneration: Imaging studies indicate potential regeneration of cartilage tissue, although long-term studies are ongoing to assess durability.
- Safety: Stem cell therapy is generally considered safe, with minimal risk of rejection or adverse effects when autologous cells (patient’s own cells) are used.
Considerations and Future Directions
- Cost: Stem cell therapy for osteoarthritis can be costly, especially when not covered by insurance. However, as research advances and techniques improve, costs may become more accessible.
- Regulatory Landscape: Regulations governing stem cell therapy vary globally. It’s essential to seek treatment from reputable clinics with a track record of safety and efficacy.
- Complementary Therapies: Integrating stem cell therapy with physical therapy and lifestyle modifications can optimize outcomes and long-term joint health.
Conclusion
Stem cell therapy represents a promising frontier in the treatment of osteoarthritis, offering potential benefits beyond symptomatic relief by targeting the underlying pathology of joint degeneration. While research continues to evolve, early findings suggest significant potential in improving joint function and quality of life for osteoarthritis patients.
If you or a loved one are considering stem cell therapy for osteoarthritis, consult with a qualified healthcare provider to explore whether this innovative approach aligns with your treatment goals and medical history. Together, we can continue to explore and harness the potential of stem cell therapy to transform the landscape of osteoarthritis management, ushering in a new era of hope and healing for those affected by this debilitating condition.