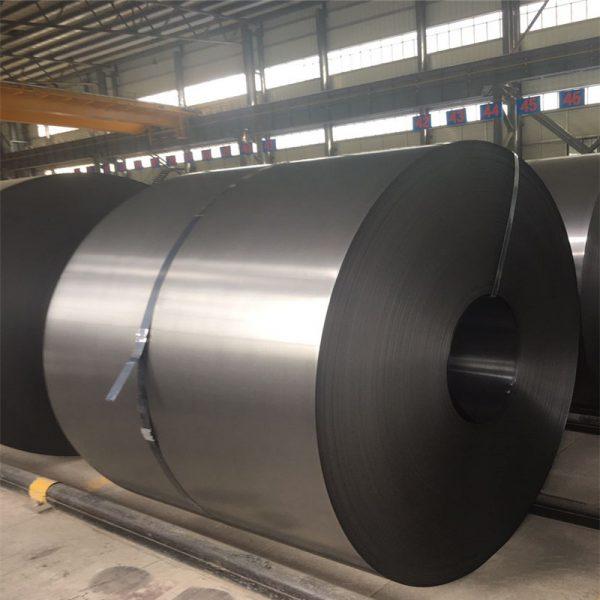
When it comes to precision engineering and construction, cold rolled steel emerges as a paramount choice. With its unique properties and superior quality, cold rolled steel offers a myriad of benefits that make it an indispensable material in various industries.
Exceptional Dimensional Accuracy
One of the primary advantages of cold rolled steel is its exceptional dimensional accuracy. Through a specialized process, the hot-rolled steel undergoes cold rolling, where it is further processed to achieve tighter tolerances and precise dimensions. This meticulous process ensures uniformity and consistency, resulting in flat, straight, and defect-free steel sheets. The dimensional accuracy of cold rolled steel enables engineers and fabricators to work with precise measurements, ensuring a seamless fit and assembly in engineering and construction applications.
Excellent Surface Finish & Uniformity
Additionally, cold rolled steel exhibits excellent surface finish and uniformity. The cold rolling process smoothens the surface of the steel, eliminating imperfections and mill scale that are often present in hot-rolled steel. The resulting surface is smooth, clean, and visually appealing, making it ideal for applications where aesthetics matter. The uniform surface finish of cold rolled steel also facilitates better paint adhesion, allowing for a flawless finish when coatings or finishes are applied.
Strength & Durability
Cold rolled steel boasts superior strength and durability. Due to the cold rolling process, the steel’s grain structure is refined, resulting in increased tensile strength and improved mechanical properties. This enhanced strength makes cold rolled steel suitable for demanding applications that require structural integrity and load-bearing capabilities. Whether it’s in construction, automotive, or manufacturing, cold rolled steel provides the strength and reliability necessary to withstand rigorous conditions and heavy loads.
Formability & Versatility
Furthermore, cold rolled steel offers excellent formability and versatility. Its enhanced ductility allows it to be shaped and formed into various intricate designs and structures. From complex architectural features to precision-engineered components, cold rolled steel can be easily manipulated without sacrificing its structural integrity. This formability makes it a preferred choice for industries that require custom fabrication and intricate designs.
Environment Friendly
In addition to its technical advantages, cold rolled steel is also environmentally friendly. The cold rolling process consumes less energy compared to hot rolling, resulting in lower carbon emissions and a reduced environmental impact. The recyclability of cold rolled steel further contributes to its sustainability, as it can be reused and repurposed without compromising its quality or performance.

Difference Between Hot rolled and Cold rolled Steel
The main difference between hot rolled and cold rolled steel can be summarized as follows:
Manufacturing Process:
The primary difference lies in the manufacturing process. Hot rolled steel is produced by heating the steel billet or slab above its recrystallization temperature and then passing it through a series of rollers to achieve the desired thickness and shape. In contrast, cold rolled steel is processed at room temperature, where the hot-rolled steel undergoes further rolling or pressing to achieve tighter tolerances and improve its surface finish.
Surface Finish:
Hot rolled steel has a rough, scaled surface due to the high temperature involved in the manufacturing process. This scale needs to be removed through processes like pickling or shot blasting. On the other hand, cold rolled steel has a smoother and more refined surface finish. The cold rolling process eliminates surface imperfections, resulting in a clean, smooth surface that is often suitable for painting or coating without any additional surface preparation.
Mechanical Properties:
Hot rolled steel tends to have a lower tensile strength and yield strength compared to cold rolled steel. This is because the hot rolling process results in a larger grain structure, which affects the steel’s mechanical properties. Cold rolled steel, on the other hand, undergoes a process of work hardening during cold rolling, resulting in increased tensile strength, hardness, and improved dimensional stability.
Dimensional Accuracy and Tolerances:
Cold rolled steel offers better dimensional accuracy and tighter tolerances compared to hot rolled steel. The cold rolling process allows for precise control over the thickness, width, and shape of the steel. Cold rolled steel is known for its consistent thickness and uniformity, making it suitable for applications that require precise measurements and tight tolerances. Hot rolled steel, on the other hand, may exhibit variations in thickness and shape due to the nature of the hot rolling process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cold rolled steel plays a vital role in precision engineering and construction. With its dimensional accuracy, superior surface finish, strength, formability, dimensional stability, and environmental benefits, cold rolled steel offers unmatched advantages over other materials. Its versatility and reliability make it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications, from architectural structures and automotive components to industrial machinery and consumer goods. When it comes to achieving precision and excellence, cold rolled steel stands as the key material for engineering and construction endeavors.